- Hakin9: E-magazine offering in-depth looks at both attack and defense techniques and concentrates on difficult technical issues.
- Exploit DB: An archive of exploits and vulnerable software by Offensive Security. The site collects exploits from submissions and mailing lists and concentrates them in a single database.
- KitPloit: Leading source of Security Tools, Hacking Tools, CyberSecurity and Network Security.
- The Hacker News: The Hacker News — most trusted and widely-acknowledged online cyber security news magazine with in-depth technical coverage for cybersecurity.
- Hacked Gadgets: A resource for DIY project documentation as well as general gadget and technology news.
- SecTools.Org: List of 75 security tools based on a 2003 vote by hackers.
- Packet Storm: Information Security Services, News, Files, Tools, Exploits, Advisories and Whitepapers.
- SecurityFocus: Provides security information to all members of the security community, from end users, security hobbyists and network administrators to security consultants, IT Managers, CIOs and CSOs.
- Black Hat: The Black Hat Briefings have become the biggest and the most important security conference series in the world by sticking to our core value: serving the information security community by delivering timely, actionable security information in a friendly, vendor-neutral environment.
- Makezine: Magazine that celebrates your right to tweak, hack, and bend any technology to your own will.
- DEFCON: Information about the largest annual hacker convention in the US, including past speeches, video, archives, and updates on the next upcoming show as well as links and other details.
- Hack Forums: Emphasis on white hat, with categories for hacking, coding and computer security.
- HackRead: HackRead is a News Platform that centers on InfoSec, Cyber Crime, Privacy, Surveillance, and Hacking News with full-scale reviews on Social Media Platforms.
- Phrack Magazine: Digital hacking magazine.
- Offensive Security Training: Developers of Kali Linux and Exploit DB, and the creators of the Metasploit Unleashed and Penetration Testing with Kali Linux course.
- Metasploit: Find security issues, verify vulnerability mitigations & manage security assessments with Metasploit. Get the worlds best penetration testing software now.
- NFOHump: Offers up-to-date .NFO files and reviews on the latest pirate software releases.
Tuesday, June 30, 2020
Top 17 Hacking Websites 2018
Thursday, June 11, 2020
HOW TO HACK WHATSAPP ACCOUNT? – WHATSAPP HACK
SO, HOW TO HACK WHATSAPP ACCOUNT?
STEP TO FOLLOW FOR WHATSAPP HACK
- Find out the victim's phone and note down it's Mac address. To get the mac address in Android devices, go to Settings > About Phone > Status > Wifi Mac address. And here you'll see the mac address. Just write it somewhere. We'll use it in the upcoming steps.
- As you get the target's mac address, you have to change your phone's mac address with the target's mac address. Perform the steps mentioned in this article on how to spoof mac address in android phones.
- Now install WhatsApp on your phone and use victim's number while you're creating an account. It'll send a verification code to victim's phone. Just grab the code and enter it here.
- Once you do that, it'll set all and you'll get all chats and messages which victims sends or receives.
WHAT IS ETHICAL HACKING
Ethical hackers must abide by the following rules-
1-Get written permission from the owner of the computer system and/or computer network before hacking.
2-Protect the privacy of the organisation been hacked etc.
Ethical Hacking and Ethical Hacker are terms used to describe hacking performed by a company or individual to help identity potential threats on a computer or network.
Read more
- Hacking Apps
- Pentest Nmap
- Pentest Vs Red Team
- Basic Pentest 1 Walkthrough
- Pentest Usb
- Is Hacking Illegal
- Pentest Owasp Top 10
- Pentest+ Vs Oscp
- Hacking Link
- Hacking Linux
- Hacking To The Gate
- Hacking Jailbreak
- Rapid7 Pentest
- Pentest Environment
- Pentest Report Generator
- Hackerx
- Pentest With Metasploit
- Hacking Tools
- Pentest Bootcamp
RECONNAISSANCE IN ETHICAL HACKING
This is the primary phase of hacking where the hacker tries to collect as much information as possible about the target.It includes identifying the target ip address range,network,domain,mail server records etc.
They are of two types-
Active Reconnaissance
Passive Reconnaissance
1-Active Reconnaissance-It the process from which we directly interact with the computer system to gain information. This information can be relevant and accurate but there is a risk of getting detected if you are planning active reconnaissance without permission.if you are detected then the administration will take the severe action action against you it may be jail!
Passive Reconnaissance-In this process you will not be directly connected to a computer system.This process is used to gather essential information without ever interacting with the target system.
Related posts
Hacking All The Cars - Part 2
Connecting Hardware to Your Real Car:
Video Walk Through Using Hardware on a Real Car
Hardware Used:
https://amzn.to/2QSmtyL
Get CANtact:
https://amzn.to/2xCqhMt
Get USB2CAN:
https://shop.8devices.com/usb2can
Creating Network Interfaces:
Summary:
Related articles
DSploit
DSploit
This is what we have under the MITM submenu:
Password sniffing
Session hijack
Redirect traffic
This feature can be used both for fun or profit. For fun, you can redirect all the victim traffic to http://www.kittenwar.com/. For-profit, you can redirect your victim to phishing pages.Replace images, videos
I think this is just for fun here. Endless Rick Rolling possibilities.Script injection
This is mostly for profit. client-side injection, drive-by-exploits, endless possibilities.Custom filter
If you are familiar with ettercap, this has similar functionalities (but dumber), with string or regex replacements. E.g. you can replace the news, stock prices, which pizza the victim ordered, etc. If you know more fun stuff here, please leave a comment (only HTTP scenario - e.g. attacking Facebook won't work).Additional fun (not in DSploit) - SSLStrip
From the MITM section of DSploit, I really miss the SSLStrip functionality. Luckily, it is built into the Pwn Pad. With the help of SSLStrip, we can remove the references to HTTPS links in the clear text HTTP traffic, and replace those with HTTP. So even if the user checks the secure login checkbox at freemail.hu, the password will be sent in clear text - thus it can be sniffed with DSniff.HTML source on the client-side without SSLstrip:
HTML source on the client-side with SSL strip:
With EvilAP, SSLStrip, and DSniff, the password can be stolen. No hacking skillz needed.
Lessons learned here
If you are a website operator where you allow your users to login, always:- Use HTTPS with a trusted certificate, and redirect all unencrypted traffic to HTTPS ASAP
- Mark the session cookies with the secure flag
- Use HSTS to prevent SSLStrip attacks
- Don't trust sites with your confidential data if the above points are not fixed. Choose a more secure alternative
- Use HTTPS everywhere plugin
- For improved security, use VPN
And last but not least, if you like the DSploit project, don't forget to donate them!
Related news
DOS (Denial Of Service) Attack Tutorial Ping Of Death ;DDOS
What is DoS Attack?
DOS is an attack used to deny legitimate users access to a resource such as accessing a website, network, emails, etc. or making it extremely slow. DoS is the acronym for Denial of Service. This type of attack is usually implemented by hitting the target resource such as a web server with too many requests at the same time. This results in the server failing to respond to all the requests. The effect of this can either be crashing the servers or slowing them down.
Cutting off some business from the internet can lead to significant loss of business or money. The internet and computer networks power a lot of businesses. Some organizations such as payment gateways, e-commerce sites entirely depend on the internet to do business.
In this tutorial, we will introduce you to what denial of service attack is, how it is performed and how you can protect against such attacks.
Topics covered in this tutorial
- Types of Dos Attacks
- How DoS attacks work
- DoS attack tools
- DoS Protection: Prevent an attack
- Hacking Activity: Ping of Death
- Hacking Activity: Launch a DOS attack
Types of Dos Attacks
There are two types of Dos attacks namely;
- DoS– this type of attack is performed by a single host
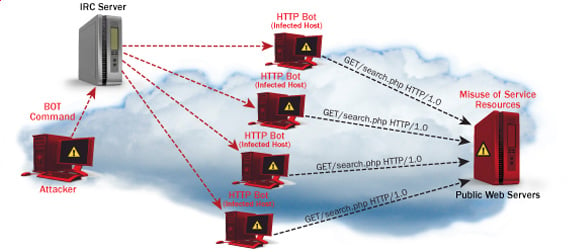
- Distributed DoS– this type of attack is performed by a number of compromised machines that all target the same victim. It floods the network with data packets.
How DoS attacks work
Let's look at how DoS attacks are performed and the techniques used. We will look at five common types of attacks.
Ping of Death
The ping command is usually used to test the availability of a network resource. It works by sending small data packets to the network resource. The ping of death takes advantage of this and sends data packets above the maximum limit (65,536 bytes) that TCP/IP allows. TCP/IP fragmentation breaks the packets into small chunks that are sent to the server. Since the sent data packages are larger than what the server can handle, the server can freeze, reboot, or crash.
Smurf
This type of attack uses large amounts of Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) ping traffic target at an Internet Broadcast Address. The reply IP address is spoofed to that of the intended victim. All the replies are sent to the victim instead of the IP used for the pings. Since a single Internet Broadcast Address can support a maximum of 255 hosts, a smurf attack amplifies a single ping 255 times. The effect of this is slowing down the network to a point where it is impossible to use it.
Buffer overflow
A buffer is a temporal storage location in RAM that is used to hold data so that the CPU can manipulate it before writing it back to the disc. Buffers have a size limit. This type of attack loads the buffer with more data that it can hold. This causes the buffer to overflow and corrupt the data it holds. An example of a buffer overflow is sending emails with file names that have 256 characters.
Teardrop
This type of attack uses larger data packets. TCP/IP breaks them into fragments that are assembled on the receiving host. The attacker manipulates the packets as they are sent so that they overlap each other. This can cause the intended victim to crash as it tries to re-assemble the packets.
SYN attack
SYN is a short form for Synchronize. This type of attack takes advantage of the three-way handshake to establish communication using TCP. SYN attack works by flooding the victim with incomplete SYN messages. This causes the victim machine to allocate memory resources that are never used and deny access to legitimate users.
DoS attack tools
The following are some of the tools that can be used to perform DoS attacks.
- Nemesy– this tool can be used to generate random packets. It works on windows. This tool can be downloaded from http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/25599/nemesy13.zip.html . Due to the nature of the program, if you have an antivirus, it will most likely be detected as a virus.
- Land and LaTierra– this tool can be used for IP spoofing and opening TCP connections
- Blast– this tool can be downloaded from http://www.opencomm.co.uk/products/blast/features.php
- Panther- this tool can be used to flood a victim's network with UDP packets.
- Botnets– these are multitudes of compromised computers on the Internet that can be used to perform a distributed denial of service attack.
DoS Protection: Prevent an attack
An organization can adopt the following policy to protect itself against Denial of Service attacks.
- Attacks such as SYN flooding take advantage of bugs in the operating system. Installing security patches can help reduce the chances of such attacks.
- Intrusion detection systems can also be used to identify and even stop illegal activities
- Firewalls can be used to stop simple DoS attacks by blocking all traffic coming from an attacker by identifying his IP.
- Routers can be configured via the Access Control List to limit access to the network and drop suspected illegal traffic.
Hacking Activity: Ping of Death
We will assume you are using Windows for this exercise. We will also assume that you have at least two computers that are on the same network. DOS attacks are illegal on networks that you are not authorized to do so. This is why you will need to setup your own network for this exercise.
Open the command prompt on the target computer
Enter the command ipconfig. You will get results similar to the ones shown below
For this example, we are using Mobile Broadband connection details. Take note of the IP address. Note: for this example to be more effective, and you must use a LAN network.
Switch to the computer that you want to use for the attack and open the command prompt
We will ping our victim computer with infinite data packets of 65500
Enter the following command
ping 10.128.131.108 –t |65500
HERE,
- "ping" sends the data packets to the victim
- "10.128.131.108" is the IP address of the victim
- "-t" means the data packets should be sent until the program is stopped
- "-l" specifies the data load to be sent to the victim
You will get results similar to the ones shown below
Flooding the target computer with data packets doesn't have much effect on the victim. In order for the attack to be more effective, you should attack the target computer with pings from more than one computer.
The above attack can be used to attacker routers, web servers etc.
If you want to see the effects of the attack on the target computer, you can open the task manager and view the network activities.
- Right click on the taskbar
- Select start task manager
- Click on the network tab
- You will get results similar to the following
If the attack is successful, you should be able to see increased network activities.
Hacking Activity: Launch a DOS attack
In this practical scenario, we are going to use Nemesy to generate data packets and flood the target computer, router or server.
As stated above, Nemesy will be detected as an illegal program by your anti-virus. You will have to disable the anti-virus for this exercise.
- Download Nemesy from http://packetstormsecurity.com/files/25599/nemesy13.zip.html
- Unzip it and run the program Nemesy.exe
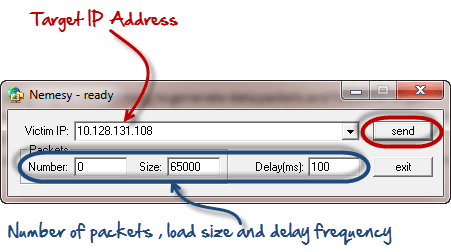
- You will get the following interface
Enter the target IP address, in this example; we have used the target IP we used in the above example.
HERE,
- 0 as the number of packets means infinity. You can set it to the desired number if you do not want to send, infinity data packets
- The size field specifies the data bytes to be sent and the delay specifies the time interval in milliseconds.
Click on send button
You should be able to see the following results
The title bar will show you the number of packets sent
Click on halt button to stop the program from sending data packets.
You can monitor the task manager of the target computer to see the network activities.
Summary
- A denial of service attack's intent is to deny legitimate users access to a resource such as a network, server etc.
- There are two types of attacks, denial of service and distributed denial of service.
- A denial of service attack can be carried out using SYN Flooding, Ping of Death, Teardrop, Smurf or buffer overflow
- Security patches for operating systems, router configuration, firewalls and intrusion detection systems can be used to protect against denial of service attacks.
More info
Wednesday, June 10, 2020
Why (I Believe) WADA Was Not Hacked By The Russians
Let's start with the main facts we know about the WADA hack, in chronological order:
1. Some point in time (August - September 2016), the WADA database has been hacked and exfiltrated
3. September 1st, the fancybear.net domain has been registered
Domain Name: FANCYBEAR.NET
...
Updated Date: 18-sep-2016
Creation Date: 01-sep-2016
5. The @FancyBears and @FancyBearsHT Twitter accounts have been created and started to tweet on 12th September, reaching out to journalists
6. 12th September, Western media started headlines "Russia hacked WADA"
The Threatconnect analysis
The only technical analysis on why Russia was behind the hack, can be read here: https://www.threatconnect.com/blog/fancy-bear-anti-doping-agency-phishing/After reading this, I was able to collect the following main points:
- It is Russia because Russian APT groups are capable of phishing
- It is Russia because the phishing site "wada-awa[.]org was registered and uses a name server from ITitch[.]com, a domain registrar that FANCY BEAR actors recently used"
- It is Russia because "Wada-arna[.]org and tas-cass[.]org were registered through and use name servers from Domains4bitcoins[.]com, a registrar that has also been associated with FANCY BEAR activity."
- It is Russia, because "The registration of these domains on August 3rd and 8th, 2016 are consistent with the timeline in which the WADA recommended banning all Russian athletes from the Olympic and Paralympic games."
- It is Russia, because "The use of 1&1 mail.com webmail addresses to register domains matches a TTP we previously identified for FANCY BEAR actors."
There is an interesting side-track in the article, the case of the @anpoland account. Let me deal with this at the end of this post.
My problem with the above points is that all five flag was publicly accessible to anyone as TTP's for Fancy Bear. And meanwhile, all five is weak evidence. Any script kittie in the world is capable of both hacking WADA and planting these false-flags.
A stronger than these weak pieces of evidence would be:
- Malware sharing same code attributed to Fancy Bear (where the code is not publicly available or circulating on hackforums)
- Private servers sharing the IP address with previous attacks attributed to Fancy Bear (where the server is not a hacked server or a proxy used by multiple parties)
- E-mail addresses used to register the domain attributed to Fancy Bear
- Many other things
The fancybear website
It is quite unfortunate that the analysis was not updated after the documents have been leaked. But let's just have a look at the fancybear . net website, shall we?Now the question is, if you are a Russian state-sponsored hacker group, and you are already accused of the hack itself, do you create a website with tons of bears on the website, and do you choose the same name (Fancy Bear) for your "Hack team" that is already used by Crowdstrike to refer to a Russian state-sponsored hacker group? Well, for me, it makes no sense. Now I can hear people screaming: "The Russians changed tactics to confuse us". Again, it makes no sense to change tactics on this, while keeping tactics on the "evidence" found by Threatconnect.
It makes sense that a Russian state-sponsored group creates a fake persona, names it Guccifer 2.0, pretends Guccifer 2.0 is from Romania, but in the end it turns out Guccifer 2.0 isn't a native Romanian speaker. That really makes sense.
What happens when someone creates this fancybear website for leaking the docs, and from the Twitter account reaches out to the media? Journalists check the website, they see it was done by Fancy Bear, they
Just imagine an expert in the USA or Canada writing in report for WADA:
"the hack was done by non-Russian, but state-sponsored actors, who planted a lot of false-flags to accuse the Russians and to destroy confidence in past and future leaks". Well, I am sure this is not a popular opinion, and whoever tries this, risks his career. Experts are human, subject to all kinds of bias.
The Guardian
The only other source I was able to find is from The Guardian, where not just one side (it was Russia) was represented in the article. It is quite unfortunate that both experts are from Russia - so people from USA will call them being not objective on the matter. But the fact that they are Russian experts does not mean they are not true ...https://www.theguardian.com/sport/2016/sep/15/fancy-bears-hackers--russia-wada-tues-leaks
Sergei Nikitin:
"We don't have this in the case of the DNC and Wada hacks, so it's not clear on what basis conclusions are being drawn that Russian hackers or special services were involved. It's done on the basis of the website design, which is absurd," he said, referring to the depiction of symbolically Russian animals, brown and white bears, on the "Fancy Bears' Hack Team" website.
I don't agree with the DNC part, but this is not the topic of conversation here.
Alexander Baranov:
"the hackers were most likely amateurs who published a "semi-finished product" rather than truly compromising information. "They could have done this more harshly and suddenly," he said. "If it was [state-sponsored] hackers, they would have dug deeper. Since it's enthusiasts, amateurs, they got what they got and went public with it.""
The @anpoland side-track
First please check the tas-cas.org hack https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=day5Aq0bHsA , I will be here when you finished it. This is a website for "Court of Arbitration for Sport's", and referring to the Threatconnect post, "CAS is the highest international tribunal that was established to settle disputes related to sport through arbitration. Starting in 2016, an anti-doping division of CAS began judging doping cases at the Olympic Games, replacing the IOC disciplinary commission." Now you can see why this attack is also discussed here.- My bet is that this machine was set-up for these @anpoland videos only. Whether google.ru is a false flag or it is real, hard to decide. It is interesting to see that there is no google search done via google.ru, it is used only once.
- The creator of the video can't double click. Is it because he has a malfunctioning mouse? Is it because he uses a virtualization console, which is near-perfect OPSEC to hide your real identity? My personal experience is that using virtualization consoles remotely (e.g. RDP) has very similar effects to what we can see on the video.
- The timeline of the Twitter account is quite strange, registered in 2010
- I agree with the Threatconnect analysis that this @anpoland account is probably a faketivist, and not an activist. But who is behind it, remains a mystery.
- Either the "activist" is using a whonix-like setup for remaining anonymous, or a TOR router (something like this), or does not care about privacy at all. Looking at the response times (SQLmap, web browser), I doubt this "activist" is behind anything related to TOR. Which makes no sense for an activist, who publishes his hack on Youtube. People are stupid for sure, but this does not add up. It makes sense that this was a server (paid by bitcoins or stolen credit cards or whatever) rather than a home computer.
The mysterious Korean characters in the HTML source
The Russians are denying it
Attribution
Let me sum up what we know:It makes sense that the WADA hack was done by Russia, because:
- Russia being almost banned from the Olympics due to doping scandal, it made sense to discredit WADA and US Olympians
- There are multiple(weak) pieces of evidence which point to Russia
- By instantly attributing the hack to the Russians, the story was more about to discredit Russia than discrediting WADA or US Olympians.
- In reality, there was no gain for Russia for disclosing the documents. Nothing happened, nothing changed, no discredit for WADA. Not a single case turned out to be illegal or unethical.
Altering the leaked documents makes no sense if it was Russia(see update at the end). Altering the leaked documents makes a lot of sense if it was not Russia. Because from now on, people can always state "these leaks cannot be trusted, so it is not true what is written there". It is quite cozy for any US organization, who has been hacked or will be hacked. If you are interested in the "Russians forging leaked documents" debate, I highly recommend to start with this The Intercept article- If the Korean characters were false flags planted by the Russians, why would they remove it? If it had been Russian characters, I would understand removing it.
- All evidence against Russia is weak, can be easily forged by even any script kittie.
Questions and answers
- Was Russia capable of doing this WADA hack? Yes.
- Was Russia hacking WADA? Maybe yes, maybe not.
- Was this leak done by a Russian state-sponsored hacker group? I highly doubt that.
- Is it possible to buy an attribution-dice where all six-side is Russia? No, it is sold-out.
Related articles
Tishna: An Automated Pentest Framework For Web Servers, Web Applications To Web Security
Tishna is complete automated pentest framework for web servers, application layer to web security.
Tishna was tested on: Kali Linux, Parrot Security OS, Black Arch, Termux, Android Led TV.
Tishna's interface: Tishna has 62 options with full automation and can be use for web security swiss knife.
Tishna's installation: First, boot your Kali Linux or Parrot Security OS up. Then open Terminal and enter these commands
Appeared:
- Cyber Space (Computer Security).
- Terror Security (Computer Security).
- National Cyber Security Services.
Brief Introduction
- Tishna is useful in Banks, Private Organisations and Ethical hacker personnel for legal auditing.
- It serves as a defense method to find as much as information possible for gaining unauthorised access and intrusion.
- With the emergence of more advanced technology, cybercriminals have also found more ways to get into the system of many organizations.
- Tishna software can audit, servers and web behaviour.
- Tishna can perform Scanning & Enumeration as much as possible of target.
- It's first step to stop cyber criminals by securing your Servers and Web Application Security.
- Tishna is false positive free, when there is something it will show no matter what, if it is not, it will give blank results rather error.
Developer
Support to the coder
You can sponsor and support via BTC.
The bitcoin address: 3BuUYgEgsRuEra4GwqNVLKnDCTjLEDfptu
Related news
DEFINATION OF HACKING
Hacking is an attempt to exploit a computer system vulnerabilities or a private network inside a computer to gain unauthorized acess.
Hacking is identifying and exploiting weakness in computer system and/ or computer networks for finding the vulnerability and loopholes.
- Pentest +
- Pentest Kit
- Hacker Language
- Hacking Games
- Pentest+ Vs Oscp
- Hacker Computer
- Pentest Tools
- Hacking Vpn
- Pentest Process
- Hacker0Ne
- Hacker Ethic
- Pentest Active Directory
- Pentest Tools For Windows
- Pentest Cheat Sheet
- Pentest Basics
- Pentest Web Application
- Pentest Windows
- Hackerone
- Pentest Process
OWASP Web 2.0 Project Update
TLDR: How Can You Help?
So, What Have We Done?
Where Are We Now?
What Is Next?
Related links
Blog Archive
-
▼
2020
(365)
-
▼
June
(30)
- Top 17 Hacking Websites 2018
- HOW TO HACK WHATSAPP ACCOUNT? – WHATSAPP HACK
- WHAT IS ETHICAL HACKING
- RECONNAISSANCE IN ETHICAL HACKING
- Hacking All The Cars - Part 2
- DSploit
- DOS (Denial Of Service) Attack Tutorial Ping Of De...
- Why (I Believe) WADA Was Not Hacked By The Russians
- Tishna: An Automated Pentest Framework For Web Ser...
- DEFINATION OF HACKING
- OWASP Web 2.0 Project Update
- Networking | Routing And Switching | Tutorial 4 | ...
- Exploit-Me
- BASIC OF CAND C++ PRograming Langauage
- TorghostNG: Make All Your Internet Traffic Anonymi...
- Fluxion - Set Up Fake AP, Fake DNS, And Create Cap...
- Potao Express Samples
- What Is Cybersecurity And Thier types?Which Skills...
- CVE-2020-2655 JSSE Client Authentication Bypass
- Setting Up A Burp Development Environment
- Masad Clipper And Stealer - Windows Spyware Exfilt...
- How To Control Android Phone From Another Phone Re...
- FOOTPRITING AND INFORMATION GATHERING USED IN HACKING
- DOWNLOAD BLACK STEALER V2.1 FULL
- Top 10 Best Google Gravity Tricks 2018
- Masad Clipper And Stealer - Windows Spyware Exfilt...
- How To Remove Write Protection From USB Drives And...
- Advanced Penetration Testing • Hacking The World'S...
- Learning Web Pentesting With DVWA Part 6: File Inc...
- ShodanEye: Collect Infomation About All Devices Co...
-
▼
June
(30)